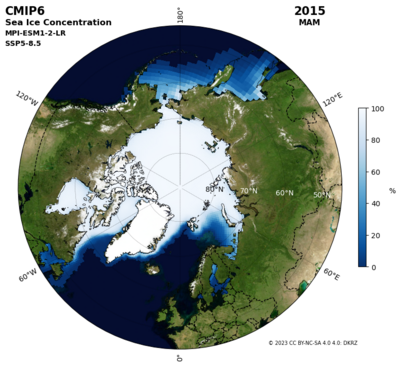
Python use a satellite image as background of an axis#
In this example we want to show i.a. how the data is processed with python-cdo, generate the panel plot using the Transverse Mercator map projection, and at the end save the figure in a PNG file. The daily surface air temperature data of the E-OBS dataset is used, further information on the data set and its download can be found in the script.
Software requirements:
Python 3
matplotlib
cartopy
python-cdo
Example script#
satellite_image_background.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
'''
DKRZ example
Polar plot of sea ice concentration data with satellite image background
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Description
In this example we demonstrate how to draw the CMIP6 sea ice concentration data
on top of the satellite image of the Earth.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Data
CMIP6 MPI-ESM1-2-LR SSP5-8.5 sea ice concentration.
Further info URL :
https://furtherinfo.es-doc.org/CMIP6.MPI-M.MPI-ESM1-2-LR.ssp585.none.r10i1p1f1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Satellite image of the Earth
The image of the Earth - The Blue Marble - with a high resolution of 0.1 degrees
(3600x1800 pixels) for August 2004 can be downloaded from the NASA Earth
Observatory download page
https://neo.gsfc.nasa.gov/view.php?datasetId=BlueMarbleNG&date=2004-08-01
To display the satellite image as map background the `CARTOPY_USER_BACKGROUNDS`
environment variable which points to the **images.json** file has to be set.
The satellite image has to be stored in the same directory as **images.json**
that will be read by Cartopy's `cartopy.mpl.geoaxes.GeoAxes.background_image()`
method.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2024 copyright DKRZ licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.en)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'''
import os
import numpy as np
import xarray as xr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.path as mpath
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
from cartopy.mpl.gridliner import LONGITUDE_FORMATTER, LATITUDE_FORMATTER
from cdo import Cdo
cdo = Cdo()
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Function: transform_to_proj()
#
# Transform function to prevent the line wrapping of data on curvilinear grids
# when `contourf` or `contour` plot style is used.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def transform_to_proj(longitude, latitude):
lat = latitude.values.ravel()
lon = longitude.values.ravel()
X, Y = [], []
for itr in range(len(lat)):
x, y = ccrs.NorthPolarStereo().transform_point(lon[itr], lat[itr], ccrs.PlateCarree())
X.append(x)
Y.append(y)
shapes = latitude.shape
X = np.reshape(X, (shapes[0], shapes[1]))
Y = np.reshape(Y, (shapes[0], shapes[1]))
return X, Y
def main():
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Path to background images and `images.json` file
#
# Tell Cartopy where to find the `images.json` file that keeps the map background
# image details.
# See https://scitools.org.uk/cartopy/docs/latest/reference/generated/cartopy.mpl.geoaxes.GeoAxes.html#cartopy.mpl.geoaxes.GeoAxes.background_img
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
os.environ['CARTOPY_USER_BACKGROUNDS'] = os.environ['HOME']+'/Python/Backgrounds'
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Sea ice concentration data
#
# Read the sea ice concentration data but use only the data on the northern hemisphere.
# This makes the computations faster. To extract the data and compute the seasonal
# means we use the Python bindings of CDO, python-cdo.
#
# Compute the seasonal means but for DJF left out the first and the last one,
# because of incompleteness. Set seasmean values equal zero to missing value.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
input_file = os.environ['HOME']+'/data/CMIP6/LR/SeaIce/Runs/ssp585/LR_SImon_EM_SICONC.nc'
input_cmd = f'-seasmean ' + \
f'-seltimestep,3/-2 ' + \
f'-sellonlatbox,0.,360.,30.,90. {input_file}'
ds_season = cdo.setctomiss('0.', input=input_cmd, returnXDataset=True)
variable = ds_season.siconc
scen_name = 'SSP5-8.5'
season_dict = {'mam': 0, 'jja': 1, 'son': 2, 'djf': 3}
# Define the order of the seasons in a dictionary and extract the season data.
season_dict = dict(mam=0, jja=1, son=2, djf=3)
var_mam = variable.isel(time=range(season_dict['mam'], ds_season.time.size, 4))
var_jja = variable.isel(time=range(season_dict['jja'], ds_season.time.size, 4))
var_son = variable.isel(time=range(season_dict['son'], ds_season.time.size, 4))
var_djf = variable.isel(time=range(season_dict['djf'], ds_season.time.size, 4))
season_data = [var_mam, var_jja, var_son, var_djf]
# Choose the time step and extract the variable data we want to show. Set values
# equal zero to NaN.
use_season = 'MAM'
use_timestep = 0
var = season_data[use_timestep].isel(time=use_timestep)
year = var.time.dt.year.data
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Plotting
#
# Choose the plot style whether to use `contour`, `contourf`, or `pcolormesh`.
# Default plotstyle is `pcolormesh`.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
allowed_plotstyles = ['pcolormesh', 'contour', 'contourf']
use_plotstyle = 'pcolormesh'
# To prevent the line wrapping for data on a curvilinear grid using contour or
# contourf plot style, we have to compute the data transformation to the
# NorthPolarStereo projection. This takes some time.
if use_plotstyle == 'contour' or use_plotstyle == 'contourf':
X, Y = transform_to_proj(ds_season.longitude, ds_season.latitude)
# Create the polar plot with the satellite image in the background.
plt.switch_backend('agg')
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,10),
subplot_kw=dict(projection=ccrs.NorthPolarStereo()))
ax.set_extent([-180, 180, 45, 90], ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.background_img(name='BlueMarbleBright', resolution='high')
ax.add_feature(cfeature.BORDERS.with_scale('50m'), lw=1., ls='--', ec='k', zorder=3)
ax.add_feature(cfeature.COASTLINE.with_scale('50m'), lw=0.5, ec='k', zorder=4)
#-- check plot style
if not use_plotstyle in allowed_plotstyles:
print(f'Warning: use_plotstyle={use_plotstyle} is not allowed. Set use_plotstyle to pcolormesh')
use_plotstyle = 'pcolormesh'
#-- common plot settings
plot_kw = dict(cmap='Blues_r', vmin=0., vmax=100.,)
#-- create data plot
if use_plotstyle == 'pcolormesh':
plot = ax.pcolormesh(var.longitude, var.latitude, var.data, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), **plot_kw)
else: #-- Note: in this case do not use transform keyword!
plot = getattr(ax, use_plotstyle)(X, Y, var.data, levels=20, **plot_kw)
#-- set circular boundary for the map from Cartopy's 'Custom Boundary Shape' example
#-- https://scitools.org.uk/cartopy/docs/latest/_downloads/b310547efca1511c5b83d11f3c6b0115/always_circular_stereo.py
theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
center = [0.5, 0.5]
radius = 0.5
verts = np.vstack([np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)]).T
circle = mpath.Path(verts * radius + center)
ax.set_boundary(circle, transform=ax.transAxes)
#-- add colorbar
cb = plt.colorbar(plot, shrink=0.4, orientation='vertical', pad=0.04)
cb.ax.get_yaxis().labelpad = 10
cb.ax.set_ylabel(ylabel='%', rotation=0.)
#-- add grid lines and annotations
gl = ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True, color='k', ls='--', lw=0.2)
gl.xlocator = mticker.FixedLocator(np.arange(-180,180,60))
gl.xformatter = LONGITUDE_FORMATTER
gl.ylocator = mticker.FixedLocator(np.arange(0,90,10))
gl.yformatter = LATITUDE_FORMATTER
gl.xlabel_style = dict(weight='normal', color='black')
gl.ylabel_style = dict(weight='bold', color='black')
#-- Note: The following grid lines ylabel redrawing maybe doesn't work within a
#-- Python script but in jupyter notebooks it does (even with same conda env)!
#
#-- Move the latitude labels from default position lon=150° to lon=87°,
#-- you need to draw the plot before doing the changes to get the gridline artist
#-- (you can get a list of the label settings with `print(gl.label_artists)`)
plt.draw() #-- important
for label in gl.label_artists:
pos = label.get_position()
if pos[0] == 150:
label.set_position([87, pos[1]])
if pos[1] > 70:
label.set_color('black')
else:
label.set_color('white')
#-- add annotations
tx = fig.text(0.1, 0.83, 'CMIP6', fontsize=16, weight='bold')
tx = fig.text(0.1, 0.81, 'Sea Ice Concentration', fontsize=12, weight='bold')
tx = fig.text(0.1, 0.79, 'MPI-ESM1-2-LR', fontsize=10, weight='bold')
tx = fig.text(0.1, 0.77, scen_name, fontsize=10, weight='bold')
tx = fig.text(0.69, 0.83, f'{year}', fontsize=16, weight='bold', ha='center')
tx = fig.text(0.69, 0.81, f'{use_season}', fontsize=11, weight='bold', ha='center')
tx = fig.text(0.61, 0.19, '© 2023 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 4.0: DKRZ', fontsize=7)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#-- save the figure to PNG
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
fig.savefig('plot_sea_ice_concentration_'+scen_name+'_satellite_image_background.png',
bbox_inches='tight', facecolor='white', dpi=100)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()